Future Of Conservation: What Is Biodiversity Finance & Where Does India Stand Globally? All You Need To Know
Writer: Ronit Kumar Singh
A confident and reliable journalist who always desires to toss the unheard voices. I cover politics and governance extensively through stories.
India, 16 Sep 2022 10:37 AM GMT | Updated 16 Sep 2022 10:57 AM GMT
Editor : Shiva Chaudhary |
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
Creatives : Ronit Kumar Singh
A confident and reliable journalist who always desires to toss the unheard voices. I cover politics and governance extensively through stories.
Biodiversity finance is the practice of managing and raising capital for biodiversity conservation. Currently, Biodiversity finance in India depends on government funds, but the focus is shifting towards sourcing capital from the private and public sectors.
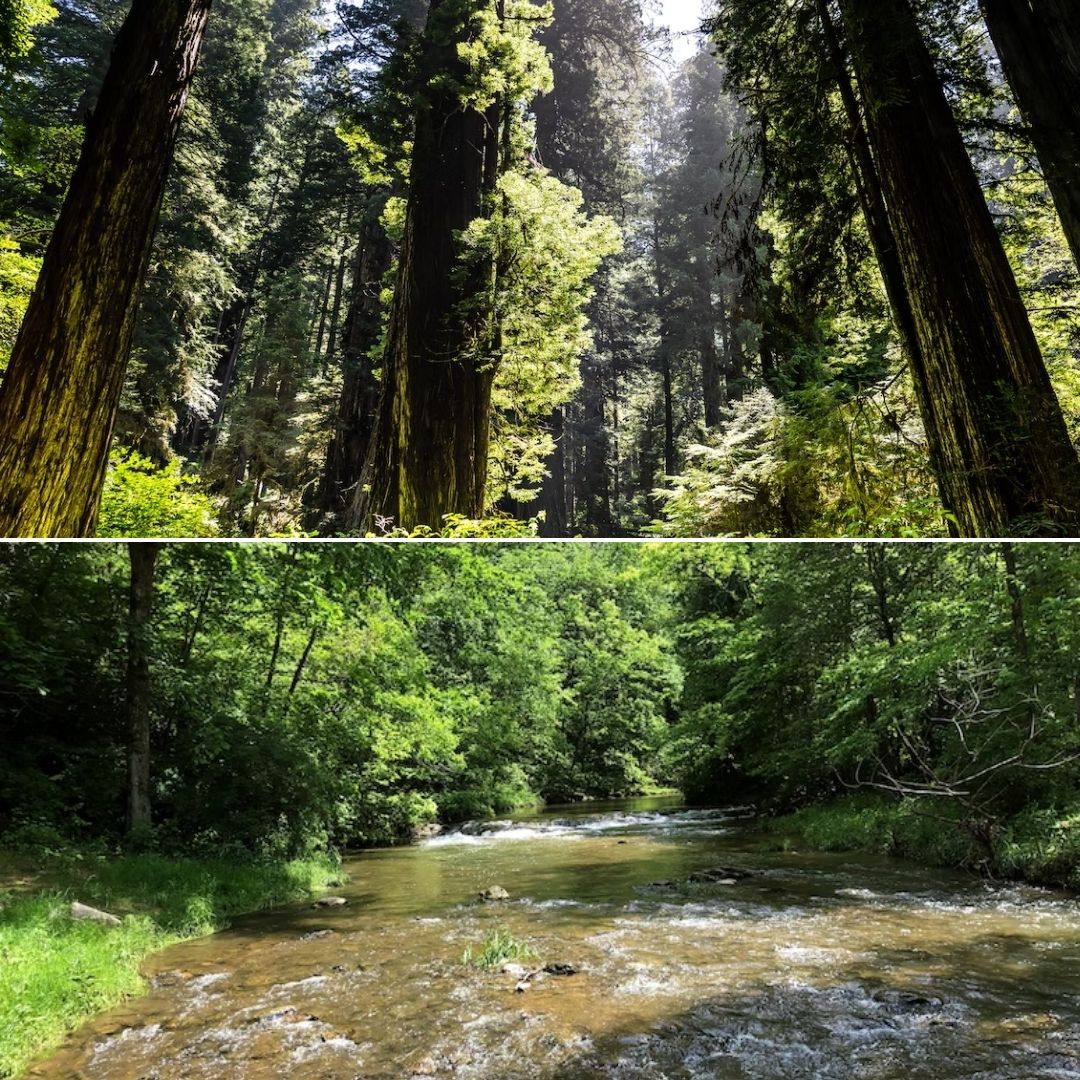
India is among the 17 mega-diversity countries of the world because of its rich species, ranking 8th on the chart. In just 2.4 per cent of the world's land area, the country features 8 per cent of all recorded species, including over one lakh species of animals and nearly 50,000 species of plants.
In today's era, when sustainable development is the global focus due to the increase in population and pollution due to several factors, biodiversity conservation becomes important as it's essential for economic growth, social development, and survival.
Biodiversity Management & Conservation In India
In India, biodiversity management is an inter-sectoral subject, and its guiding principles are provided by the National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP). Any sector requires proper finance management for its exponential growth, and biodiversity conservation is no exception.
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change is the nodal ministry responsible for funding and arranging resources. Furthermore, there are also 24 other ministries in India whose programs, schemes and activities impact biodiversity conservation. Different states and union territories also contribute to arranging resources for the same.
What Is Biodiversity Finance?
Biodiversity finance is a term used to describe the practice of raising and managing capital and funds for biodiversity conservation. It comes under the umbrella terms of conservation finance, which aims to fund for conservation of water, land, and other natural resources in a sustainable manner.
Until now, only nodal ministries and other government agencies were responsible for funding and managing the country's biodiversity conservation. But with the passing years, the focus is gradually shifting toward sourcing financing from private and public sectors.
Raising funds and capital from private and public sectors includes finance mechanisms such as tourism taxes, conservation trust bonds, green bonds, environmental services payments, and nature swaps debt. The effort is to develop a medium to quantify the finance gap in biodiversity conservation and bridge the same.
Where Does India Stand?
According to a report published by the Wildlife Institute of India, the finances for conservation in the country between 2016-17 came from 116 schemes and 24 ministries to nearly $2.64 billion. Meanwhile, a biodiversity conservation finance assessment report for implementing NBAP suggests that India needed $12 billion annually during the same period. The data signifies that India lacked nearly $9 billion to meet the financial requirement for implementing NBAP.
In another report published by India Spends, the data showed that India needed $16.5 billion for biodiversity conservation during 2017-22; the country only had $10 billion for managing finances and investment. However, the good sign for the country is that private finances are exponentially growing. In 2014, India also became the first country to legally mandate CSR activities under Section 135 of the Companies Act.
 All section
All section