Image Credits: Outlook
IIT Guwahati Researchers Develop Efficient Method To Harvest Water From Air
Writer: Ankita Singh
A literature lover who likes delving deeper into a wide range of societal issues and expresses her opinions about the same. Keeps looking for best-read recommendations while enjoying her coffee and tea.
Assam, 22 Dec 2020 11:18 AM GMT
Editor : Prateek Gautam |
A free soul who believes that journalism, apart from politics, should stand for social cause and the environment.
Creatives : Rajath
A free spirit who find meaning in life with the virtue of creativity and doing job par its excellence, animal lover and traveller by heart.
The researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Guwahati, have developed novel materials that can efficiently harvest water from humid air. The research done by them has also been published in the international journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Guwahati, have developed novel materials that can efficiently harvest water from humid air. The research done by them has also been published in the international journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
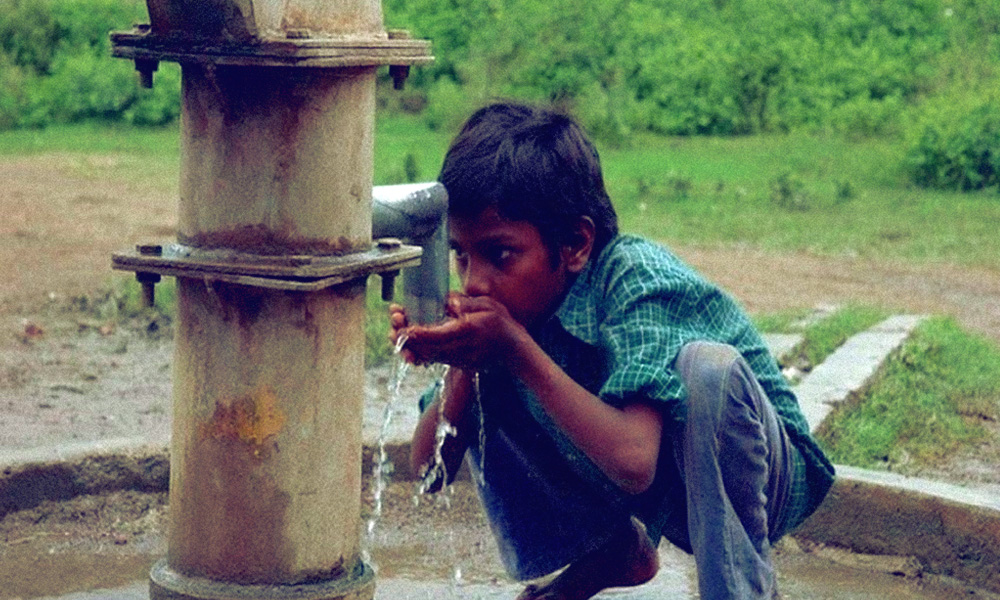
As water scarcity is a major concern in various parts of the world, there have been attempts to collect and conserve water through non-traditional means. Many scientists have turned to nature to design ways of water harvesting.
Uttam Manna, Associate Professor at IIT Guwahati's Centre of Nanotechnology, said that in regions across the world which naturally receive scanty rainfall, plants and insects had devised ingenious strategies to pull and collect water right out of the air. Mimicking the same technique, scientists worldwide are trying to build technologies that can pull out water from thin air.
He also said such water-harvesting techniques use the concept of hydrophobicity or water-repelling nature of some materials. Explaining the concept of hydrophobicity, Manna said that it could be understood by looking at the lotus leaf.
The lotus leaf is water repellent because there is a layer of trapped air between the leaf surface and the water droplet. This nature of the leaf causes the droplet to slide off the leaf.
The researchers at IIT-Guwahati have used the concept of chemically patterned SLIPS for the first time and used it effectively to harvest water from moist air. According to the researchers, this water harvesting interface is highly efficient, where the fog collecting rate is really high.
Manna said that when this method of water harvesting was compared to the performance of their pitcher-plant inspired materials or other bio-inspired ideas, the researchers found it comparatively better in terms of efficiency.
Manna remarked that at present, more than 50 per cent of India's population have no access to safe drinking water, and every year, around 200,000 people die due to shortage of drinking water.
He further added that this inexpensive method for harvesting water from water vapour or fog droplets in the air could potentially alleviate the water scarcity issues in the country.
The team of researchers also included research scholars Kousik Maji, Avijit Das and Manideepa Dhar.
Also Read: Odisha Farmer's Innovative Seed-Extractor Cuts De-Seeding Time Of Vegetables By Over 60%
 All section
All section